Turkey
WHAT IS THE GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION OF TURKEY?
The Geographical Location and Characteristics of Turkey
Turkey is located in a strategical region in the Northern Hemisphere, where old world continents, mostly come close to each other. Correspondingly, the mathematical and unique position of Turkey influences the social, political and economical situation of it.
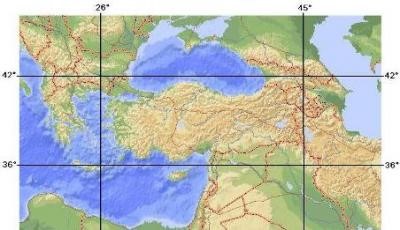
THE GEOPOLITICAL POSITION OF TURKEY AND ITS OUTCOME
Turkey is both an Asian and a European country thanks to its geographical position.
Located in the junction point of Asia, Europe and Africa, our country is like an economical, social, political and cultural bridge.
Also, the country has a central position among the Balkans, the Caucasia and the Middle East.
Turkey carries great importance with the Bosporus and the Dardanelles. It is necessary for the countries located around the Black Sea to use the straits and seas around Turkey, so this increases the importance of the straits.
Climate variability, soil diversity and land structure which can be changeable even in short distances cause rich plant diversity and creation of important water resources throughout the country. As a consequence, a natural environment occurs suitably for human life.
These circumstances have provided our country the opportunities to supply the needs in terms of agricultural production.
Apart from the geographical advantages, dynamic young population with high rate of education is one of the most important advantages of Turkey.
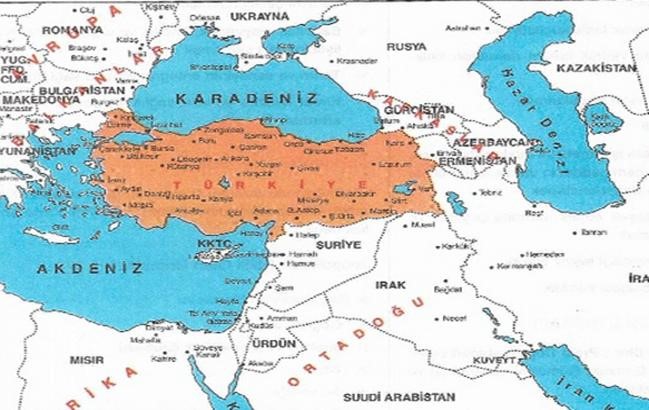
GEOGRAPHICAL FORMATIONS OF TURKEY
Turkey is in the Alpine Folding zone, which starts from the Pyrenees in the West and reaches to the Himalayas in the East. The Russian-Siberian old masses in the North and the African-Arabian old masses in the South have great roles in the formation of the Turkish part of this huge folding zone. Mountain ranges in the North and the South (Northern Anatolia and the Toros Mountains) which belong to the Alpine Folding zone have roles on the designation of the baselines of the current surface features of Turkey.
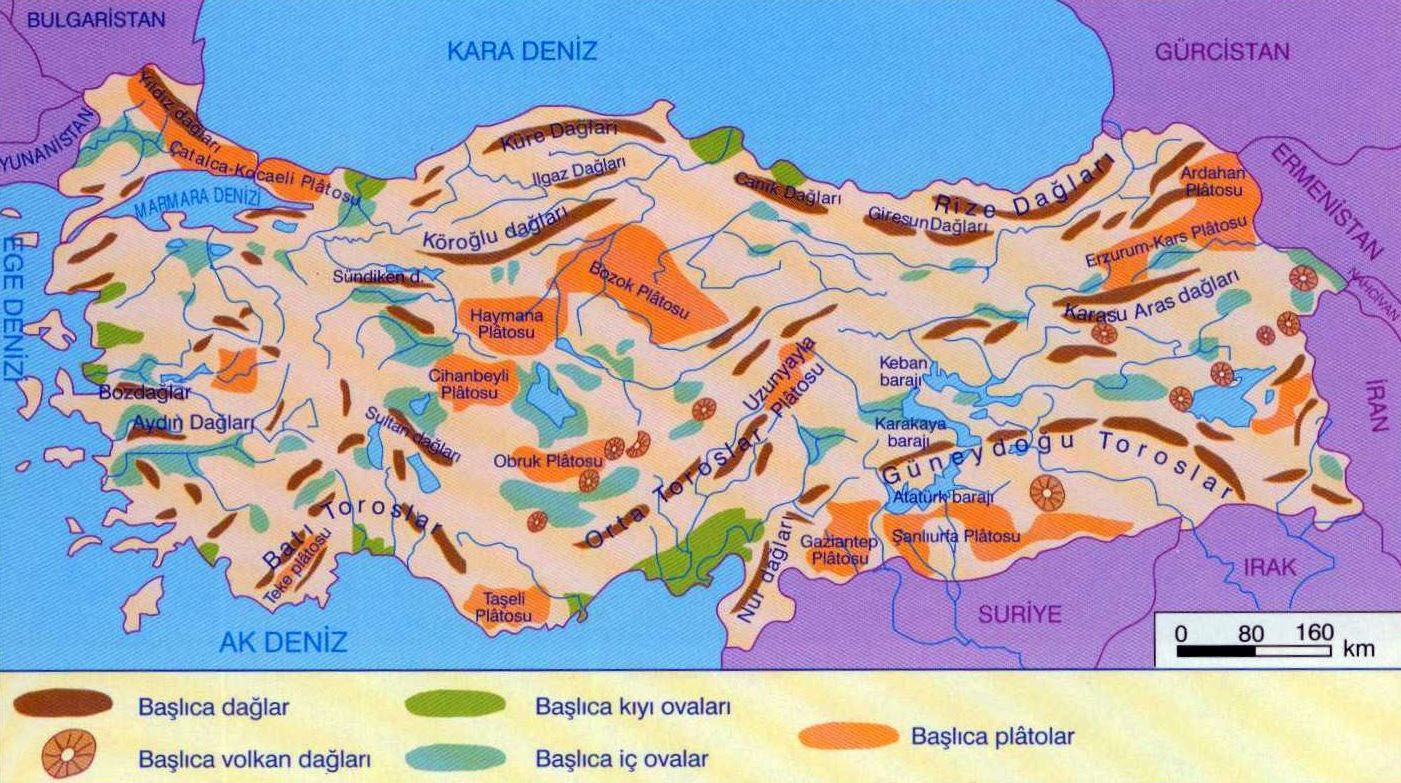
MOUNTAINS AND PLAINS
Turkey is a high country where geographical formations show the variety (average height: 1130m). According to the variety of height steps, the dispersion of the lands in Turkey are: the heights between 0-250m form 8% of Turkey’s square, the heights between 250-500m form 9.5% of Turkey’s square, the heights between 500-1000m form 27% of Turkey’s square, the heights between 1000-1500m form 30% of Turkey’s square, the heights between 1500-2000m form 15.5% of Turkey’s square and the heights more than 2000m form 10% of Turkey’s square. As it can be inferred from these numbers, more than half of the land in Turkey (55.5%) is more than 1000m. The heights between 0-250m specify the coastal lands, the heights between 250-500m specify the plains and hills behind the coastal lands, the heights between 500-1000m specify the transition areas from plains to mountains. As the largest geographical region of our country, Central Anatolia Region’s average height is over 1000m and the average height of the Eastern Anatolia Region is more than 1500m (height increases from the West to East).



RIVERS
Watershed, which separates the river basins lengthens roughly in the direction of northeast-southwest in Turkey. Among the rivers located in the east of this line, the Euphrates and the Tigris empty into the Persian Gulf and the Aras River and the Kura River empty into the Caspian Sea, the rivers located in the west of this line empty into the Black Sea (the Sakarya River, the Filyos River, the Kızılırmak River, the Yeşilırmak River, the Doğankent River, the Çoruh River) and the Simav River empties into the Sea of Marmara. Also, the Morista River, the Bakırçay River, the Gedik River, the Little Maeander River and the Greater Menderes River empty into the Aegean Sea and the Aksu River, the Manavgat River, the Göksu River, the Tarsus River, the Seyhan River, the Ceyhan River and the Orontes River empty into the Mediterranean. The primary drainage basins of the rivers in Turkey are the Black Sea, the Mediterranean, the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf and the closed basins of the Central Anatolia and Lake Van. Among these; the Black Sea basin covers 31.5% of the land of Turkey, the Persian Gulf basin covers 23.5% of the land of Turkey, the Mediterranean basin covers 13% of the land of Turkey, the Aegean Sea basin covers 10.5% of the land of Turkey, the Sea of Marmara basin covers 3.5% of the land of Turkey and the closed basins (basins of the Central Anatolia and Lake Van) covers 13.5% of the land of Turkey.
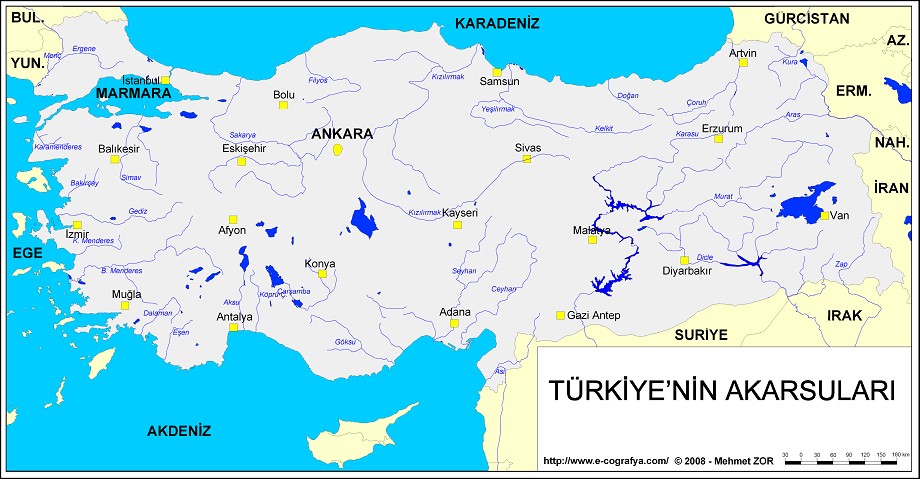

IMPORTANT MOUNTAINS, RIVERS, LAKES, DAMS AND ISLANDS
MOUNTAINS
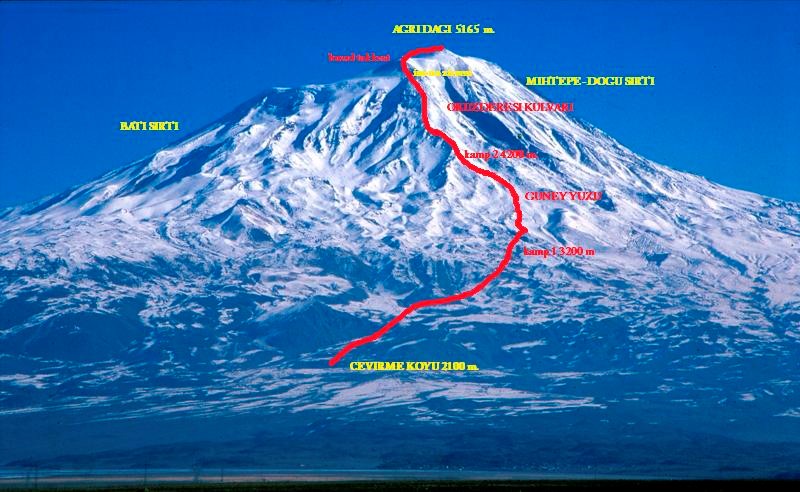
Mount Ararat 5137m
Mount Suphan 4058m
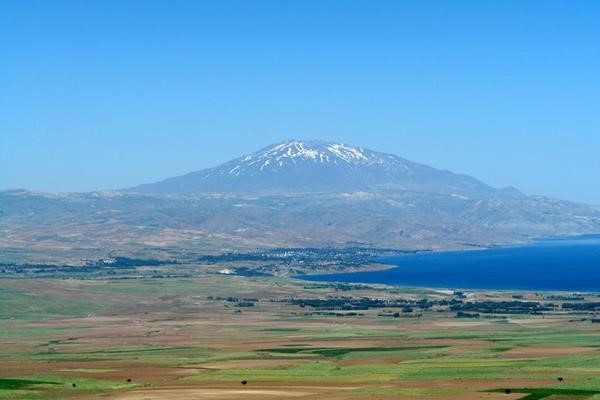

Mount Kackar 3932m

Mount Erciyes 3917m

Mount Kalkanlı 2652m
Mount Uludağ 2543m
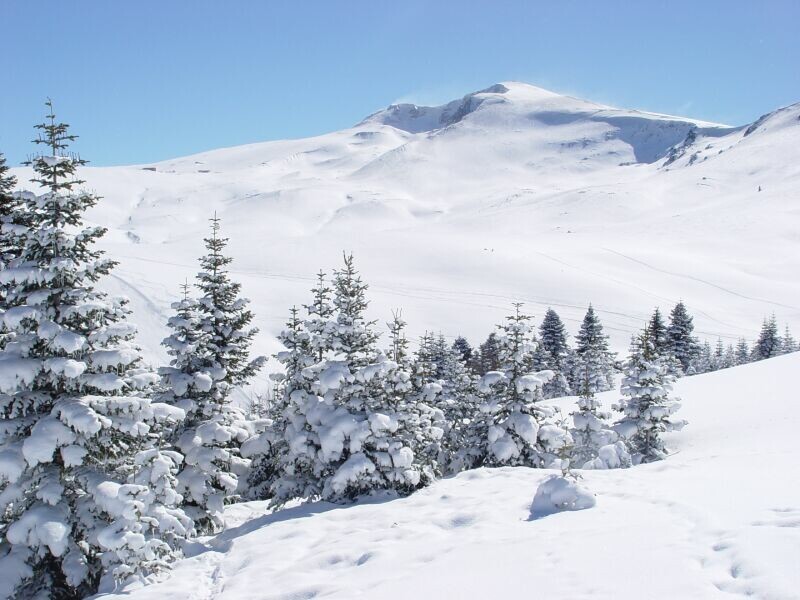

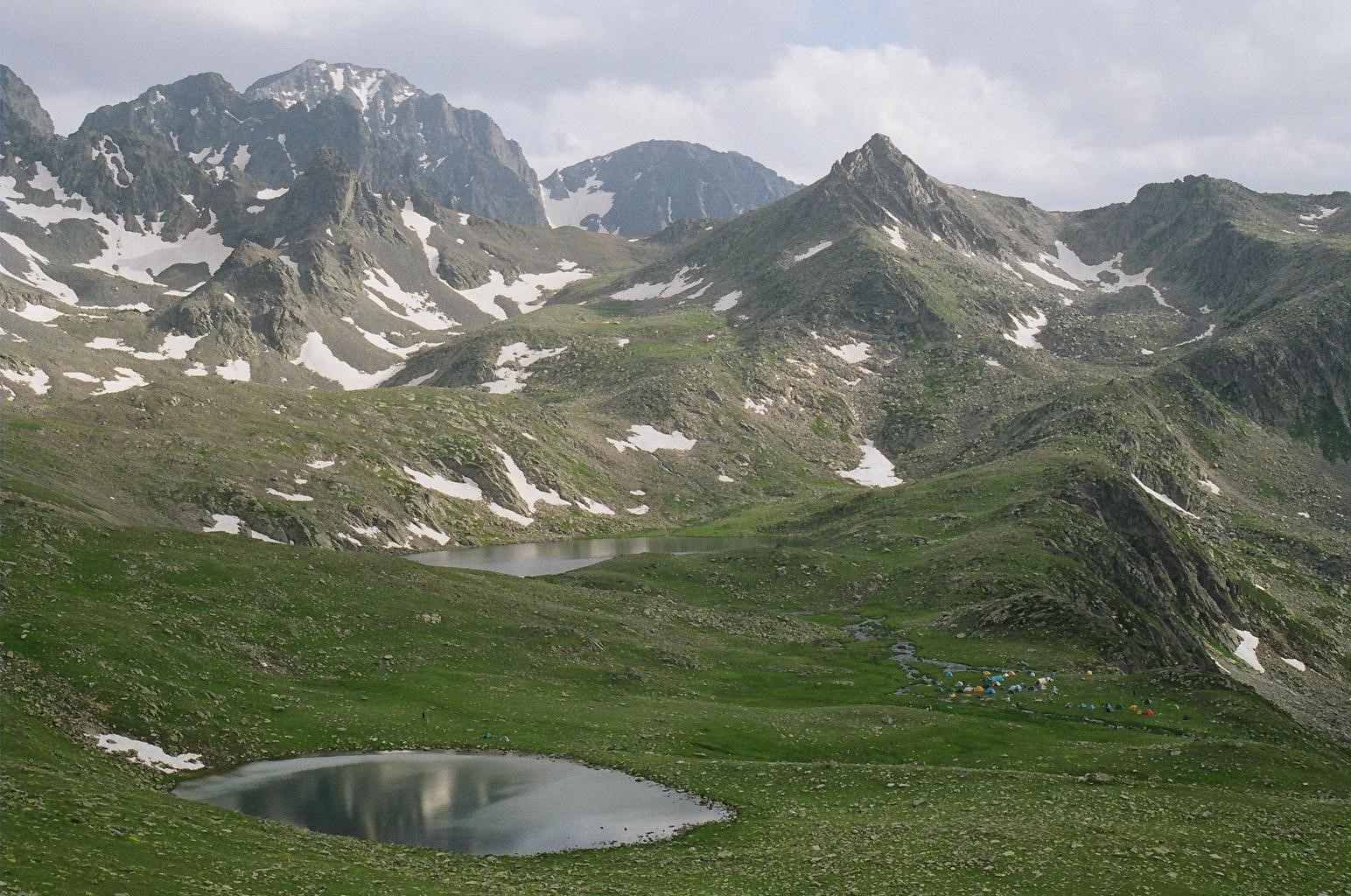
RIVERS
The Kızılırmak River 1355km

The Euphrates 1263km
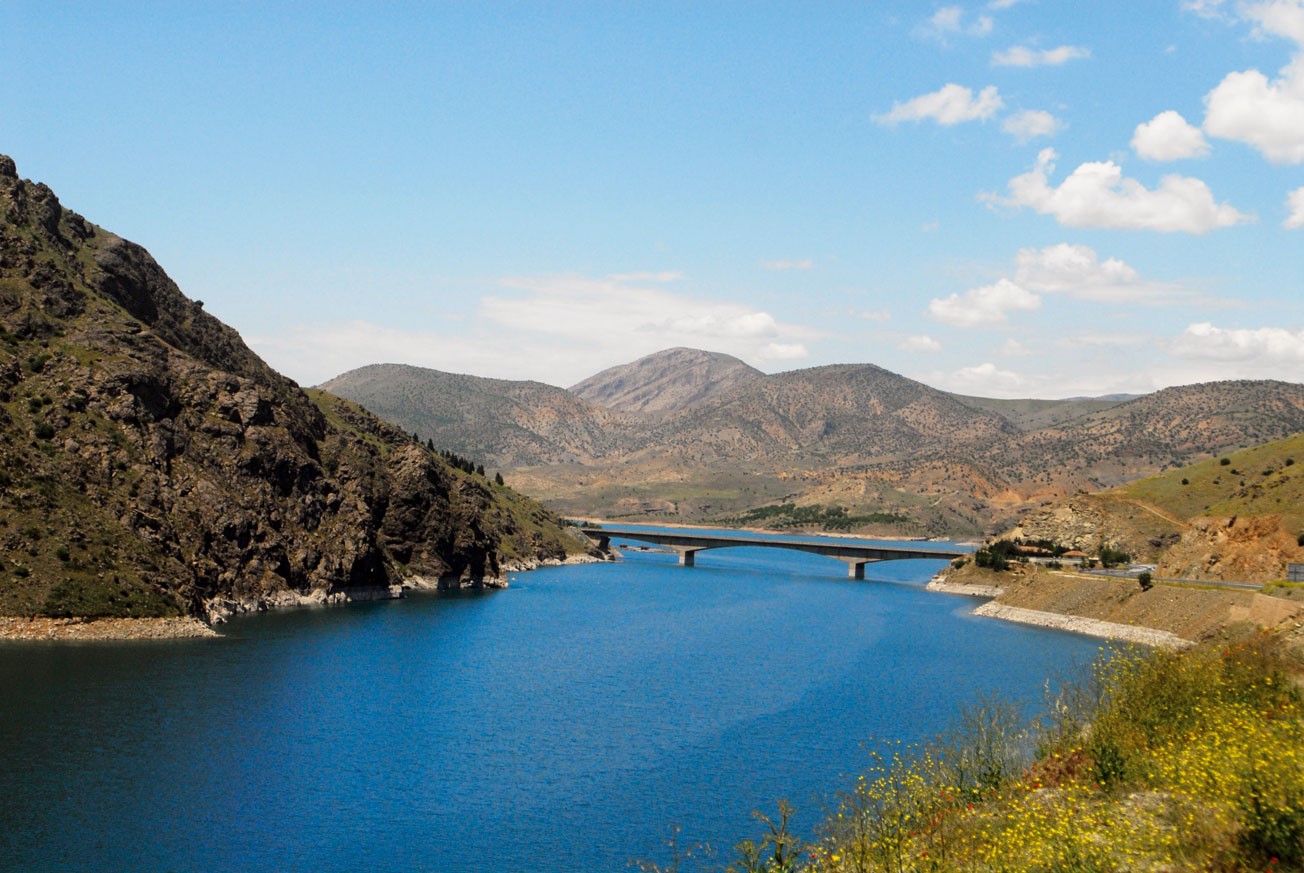

The Sakarya River 824km

The Seyhan River 560km

The Aras River 548km
The Tigris 523km
The Yeşilırmak River 519km

The Ceyhan River 509km
LAKES
Lake Van 3.800km²

Lake Tuz 1.600km²

Lake Beyşehir 730 km²

Lake Eğirdir 480 km²
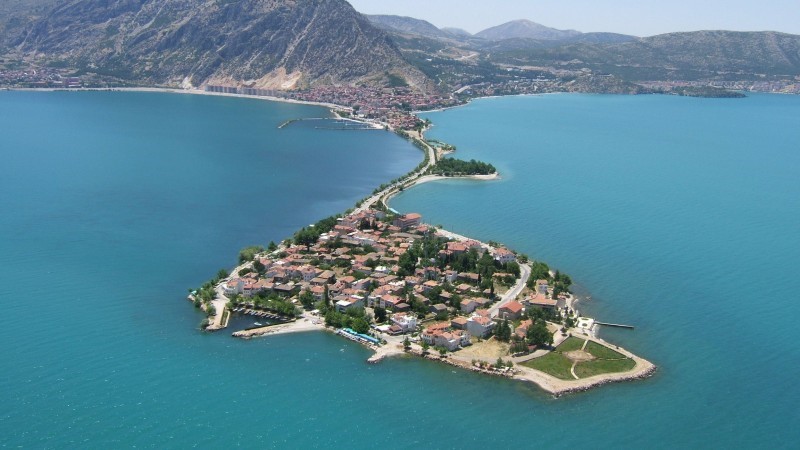

DAMS
Atatürk Dam 817 km²
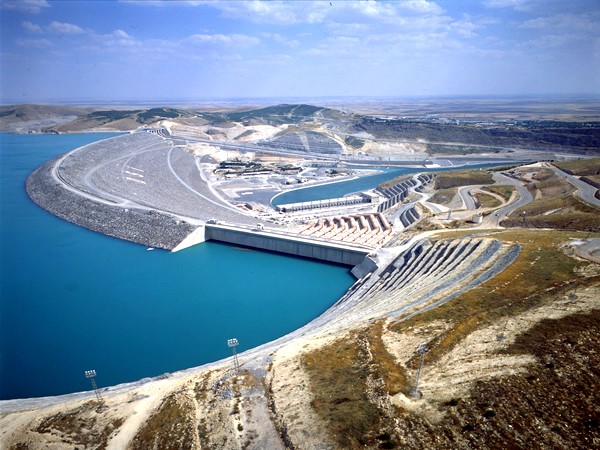

Keban Dam 675km²
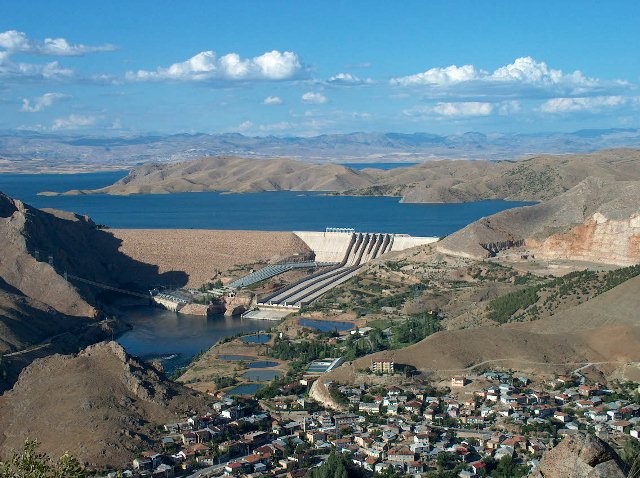

Karakaya Dam 268km²
Hirfanlı Dam 263km²
Altınkaya Dam 263km²
ISLANDS
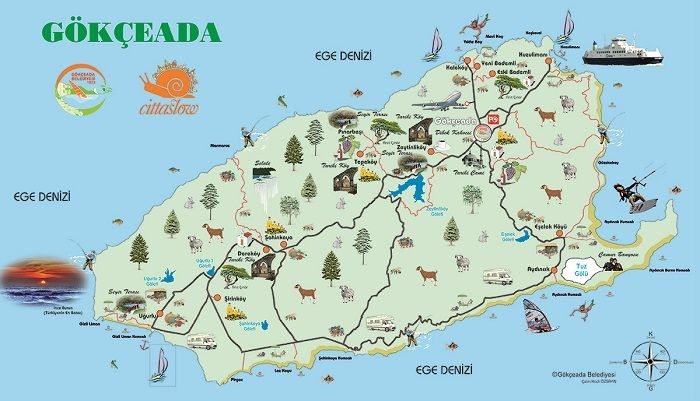
Gökçeada Island 279 km²
Marmara Island 117 km²
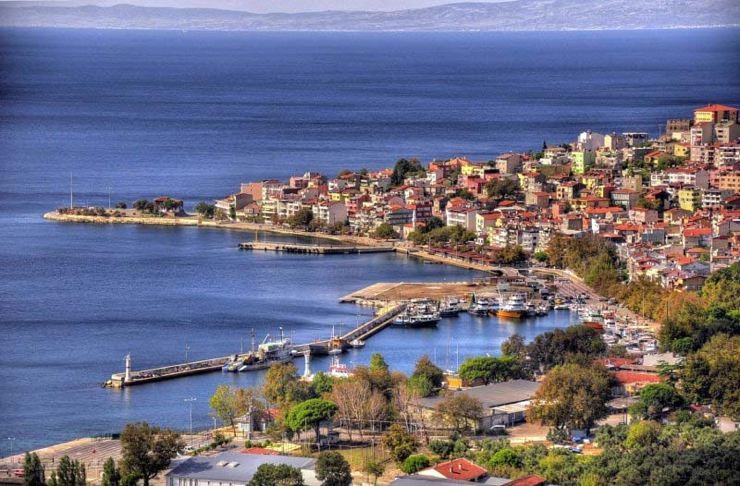

Bozcaada Island 36km²

İmralı Island 9.9km²
THE POPULATION OF TURKEY
According to Turkish Statistical Institute, the population of Turkey is 77.695.904 as a result of the population census conducted in 2014. 1.337.504 babies were born in 2014. Among these babies, 687.255 babies were boys, and 650.249 babies were girls. 390.121 people died in 2014, and among the deseased, 213.231 people were men, and 176.890 people were women.
In 5-year period between 2009 and 2014, the population in 67 cities increased, but it decreased in 14 cities. The population of the whole country increased 7.07% proportionally. The population of Antalya has increased most by 15.77% out of 81 cities proportionally. However, Istanbul showed the highest increase by 1.461.860 people in number. In addition, Yozgat became the city whose population decreased most by 11.24%.
LANGUAGE
The official language of Turkey is Turkish. Turkish which is an agglutinative language forms Altaic language family with Mongolic, Tungusic, Koreanic and Japonic languages. Turkish is the fifth most spoken language which is spoken from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean in the west, the Arctic Ocean in the north, the Persian Gulf in the south with Turkish dialects which are approximately spoken by 220 million people. The first sources of the written Turkish language were Orkhon inscriptions which originated in 7th and 8th centuries. Its development in Anatolia dates back to 13th century. Turkish which has the most speakers in number among Turkish written languages is spoken by over 75 million people as a language of speaking, writing, teaching, science, culture and art. In its history, Gokturk, Uyghur and Arabic alphabets were used. However, with the Alphabet Revolution which was made by Atatürk in 1928, people started to use the new Turkish Alphabet which was suitable for the Turkish sound scheme.
GEOGRAPHICAL REGIONS
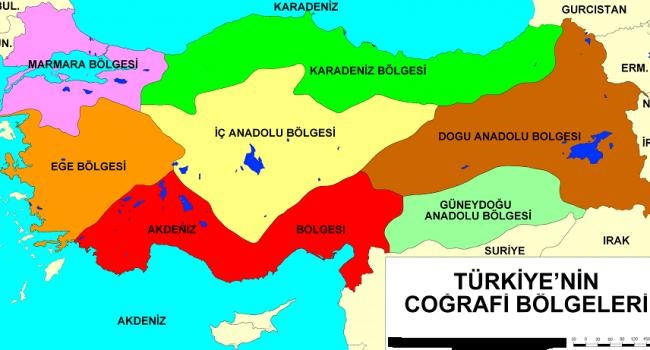
The geographical regions of Turkey comprise seven regions which were originally defined at the country's First Geography Congress in 1941. The seven official geographical regions are the Marmara Region (9.32%), the Black Sea Region (14.81%), the Aegean Region (11.50%), the Mediterranean Region (11.54%), the Central Anatolia Region (24.04%), the Eastern Anatolia Region (19.18%), and the South-eastern Anatolia Region (9.61%).
THE GLOBAL TURKISH INDUSTRY
Today, there is a worldwide manufacturing, which bases its production on imports. The integration of Turkey’s import industry and the global economy began in 1980 by adopting the growth policy based on exports, and it became strong by the reconstruction after the crisis in 2001 and Customs Union Agreement with EU. In Turkey, people concentrate on jobs that aim of increasing productivity, the share in the added value and the power in international competing power of small and medium sized enterprises (SME).

RELIGIOUS LIFE
Islam is the largest religion in Turkey with 99% of its population being Muslim, and the rest of the people are either Jewish or Christian that belong to different sects. Everyone in the country has the freedom of religion and belief. Constitutionally, nobody can be forced to participate in a religious ceremony, share his or her own religious belief and worship. In addition, people cannot be charged because of their religious beliefs or be constrained from worship. The religious understanding of Turkish people is based on the Quran which states that the religions and beliefs are the individual preferences between the God and them, and there cannot be any kind of pressure in religion. This doctrine in religion has transformed into tolerance and hospitality which have developed throughout the centuries. 233 churches and 31 synagogues are still open in Turkey. As a result of its nature of being a multi-religious society, it is possible to see the shrines of 3 major world religions side by side which is less likely to be seen in other societies.





